Zapier Growth Story - 10Mn Users and $250Mn Revenue in 12 Years with just $2.6M investment
In this edition, we dive into Zapier’s key growth strategies, including programmatic SEO, freemium pricing, content marketing, and strategic partnerships.
In 2019, I was trying to automate a sequence of emails from my Excel sheet based on the user onboardings we were doing at ReFier. I didn’t actually know how to go about it.
One of my friends told me to look at Zapier.
Gosh! As I searched on Google, I went deep into a rabbit hole and learned at least 10 different zapier automations that I could use in our marketing and operations.
Zapier was always at the top of my list of companies to research deeply and understand their playbooks.
Last week, I decided to write the next newsletter on Zapier's Growth Journey.
When I saw their first interview, I was shocked…
$250M+ in revenue in 11 years with just a $2.6M investment.
This is real OG work…
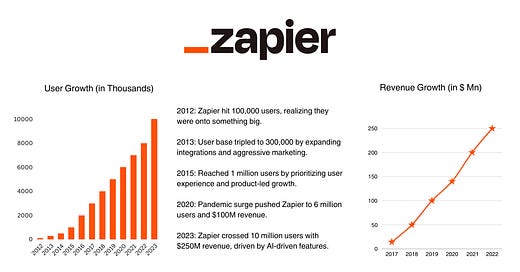
Growth Journey - Crossed 10Mn Users and $250Mn Revenue in 12 Years
Zapier’s journey is a masterclass in scaling a product that solves real problems. From its launch in 2011, Zapier’s user growth has been nothing short of extraordinary. Let’s walk through how they grew year by year.
2011: Zapier was launched with a simple yet powerful idea: automate workflows between web applications.
- Initially growth was slow. The market was still getting used to the concept of automation, and Zapier had to prove its worth. The entire focus was on building a stable product with a small but dedicated user base.
- Instead of chasing revenue early, they invested in creating a product that users loved.
2012: By the end of 2012, Zapier hit 100,000 users.
- This was the point when they realized they were sitting on something truly big..
- What actually worked was their focus on expanding app integrations and aggressive marketing to early adopters and tech-savvy users.
2013: The user base tripled to 300,000 Users.
- 3x growth isn’t normal in 12 months… There was a growing demand for SaaS tools and integrations. They shipped more integrations, partnered with app developers, doubled down on marketing efforts and got solid word of mouth from satisfied users.
Strategic Choice - Integration Expansion
2014: Crossed Half a Million (500K) users. 2x growth again in 12 months
- This time they leveraged the growing awareness of automation tools and rode on the tail winds of SaaS adoption.
2015: Grew 2x again and hit 1 million users.
They prioritized user experience and adopted product-led growth strategies. That enabled the product itself to be the key to acquisition. Also ramped up content marketing efforts, which drove new user acquisition.
Strategic Choice - Product led Growth
2016: The user base again doubled within a year in 2 Mn.
- They introduced new features and integrations for both individual users and enterprises. And introduced a freemium pricing model.
Strategic Choice - Freemium Model Introduction
2017: 3 Million Users and $14.4M Revenue
- They started feeling heat from the competition as new tools started emerging. They invested heavily in improving customer support and ensuring a seamless user experience. They also ramped up their community engagement for building a loyal user base that advocated for the brand.
2018: Steady Climb to 4 Million Users.
- Continued investment in marketing and strategic partnerships, coupled with a focus on refining the onboarding process and reducing churn.
2019: A Major Milestone - Zapier hit 5 million users and $50M Revenue
- Strong adoption among businesses for automating routine tasks, but market saturation and competition made it harder to acquire new users at the same rate.
- They focused on enhancing product features that differentiated Zapier from competitors, along with targeted marketing campaigns to specific industries and user segments.
2020: The Pandemic Surge - 6 Million Users and $100M Revenue
- The pandemic accelerated digital transformation, pushing Zapier’s user base to 6 million.
- Growth spiked again because of: Increased reliance on remote work tools and businesses sought efficiency through automation. Zapier responded quickly by offering resources and support to help new users get started with automation in a remote work environment.
Strategic Choice - Build Fast and Release
2021: Zapier surpassed 7 million users and $140M Revenue
- Focused on expanding their integration ecosystem and improving customer success initiatives to ensure that new users stuck around and found long-term value in the platform.
Strategic Choice - Education and Community
2022: 8 Million Users and about to cross $200M Revenue
- Growth at a flat pace because of maturity in the market and increased competition.
- They expanded into new verticals and industries, tailoring their messaging and features to specific use cases. This year was also about refining the product based on extensive user feedback.
2023: Crossed 10 Million Users globally with $250M Revenue at a 26.12% growth rate
- Focus on proven playbooks of what worked in the last 12 years i.e. continued focus on product innovation, customer education, and expanding the integration library to meet the evolving needs of their user base.
- Developed and launched AI-driven features that simplified complex workflows.
Strategic Choice - AI enabled automation
Zapier’s growth story isn’t just about numbers; it’s about strategic decisions, responding to market dynamics, and staying ahead of the competition.
Challenges and Obstacles in Zapier’s Journey
Zapier’s growth story is undoubtedly impressive, but like any successful company, it has faced its share of challenges along the way.
Here’s a closer look at some of the key challenges Zapier has encountered.
Challenge 1 - Bugs and Integration Issues
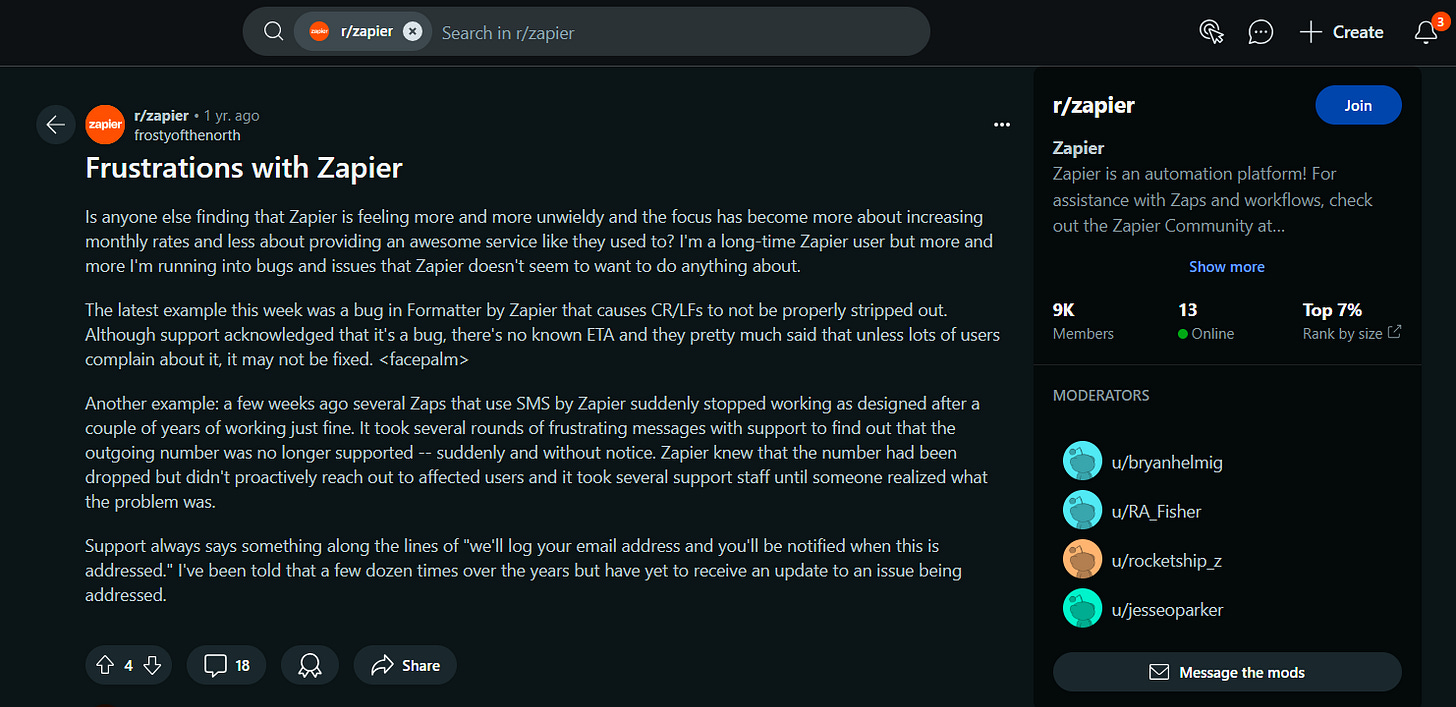
Microsoft Sharepoint App Breakdown: One notable issue occurred when the Microsoft Sharepoint app stopped working. Users were left hanging for 4-5 days before Zapier support responded, “it’s a known issue and we are working on it”.
- Impact: This delay not only frustrated users but also highlighted the need for more proactive communication from the support team.
Formatter Tool Bug: Another challenge arose with Zapier’s Formatter tool, where a bug caused issues with CR/LF stripping.
And what was the response from support? - “We are fixing and it’s taking time”
- Impact: This approach to bug fixing can erode user trust, especially when they feel their concerns aren’t prioritized.
SMS Integration Failure: Several users faced a major hurdle when their SMS by Zapier Zaps suddenly stopped working after years of reliability.
The cause? An outgoing number was no longer supported, but support was slow to identify and communicate the issue.
- Impact: This led to a significant drop in confidence among users who relied on these Zaps for critical notifications.
Challenge 2 - Declining Customer Satisfaction
As Zapier has grown, so too have the expectations of its users.
Perception of Losing Focus: Some users feel that Zapier has become harder to use and more focused on raising prices than maintaining the great service they once had.
- Impact: This shift in perception was dangerous, as long-time users started looking for alternatives when they felt they weren’t getting value for their money.
Frustration with Bug Fixes: Users have expressed frustration over bugs and issues that seem to persist without resolution. Support teams often say they’ll log the issue, but updates are always time taking and no acknowledgement on the timelines.
- Impact: This can create a sense of helplessness among users, who might feel their concerns are not being taken seriously.
Switching to Competitors: The dissatisfaction has been strong enough for some users to switch to competitors like Make. Complaints range from the platform not providing enough value to the cost, to simple but unresolved issues causing daily frustration.
- Impact: Losing users to competitors is a clear sign that addressing these issues is critical for Zapier’s continued success.
Challenge 3 - Outages and Downtime
No software is immune to outages, but how a company handles them can make all the difference.
SMS Service Outage: A recent incident involved Zapier’s SMS service going down, with users seeing false positives in their Zap history (showing SMSes being sent when they weren’t). Worse, Zapier didn’t proactively inform affected users.
- Impact: This not only disrupted workflows but also led to trust issues. Users depend on the reliability of the platform, and outages, coupled with poor communication, can severely damage that trust.
Challenge 4 - Initial Product Limitations
Pay-to-Use Problems: Initially, Zapier operated on a pay-to-use model, which limited its user base. The barrier to entry was high, and this made it difficult to attract new users who were hesitant to pay upfront for a service they had not yet experienced.
- Impact: This model stifled growth, as fewer users were willing to take the risk without trying the platform first.
Challenge 5 - Market Competition and Positioning
Crowded Market: When Zapier entered the market, it faced stiff competition from established players like IFTTT and other integration tools. Differentiating itself in a space where users already had alternatives was a tough task.
- Impact: It was challenging to establish a strong brand presence and convince users to switch from tools they were already familiar with.
Establishing Demand: While there was a clear need for integration solutions, Zapier had to actively demonstrate its value to potential users. This meant engaging in extensive outreach and connecting with communities where users expressed frustration with the lack of integration options.
- Impact: Establishing demand required significant effort and time, as Zapier needed to convince users of the platform’s value proposition.
Challenge 6 - Building a Developer Ecosystem
Scalability of Integration: Initially, Zapier built integrations manually. While this worked at first, it quickly became clear that this approach was not scalable as the number of users and their demands increased.
- Impact: Manual integration development was time-consuming and limited the speed at which Zapier could grow its offerings.
Creating Network Effects: Establishing a robust developer ecosystem was essential for generating network effects. However, attracting enough developers to build integrations and make Zapier indispensable to users was a significant challenge.
- Impact: Without a strong developer community, Zapier risked falling behind in the race to offer comprehensive integration solutions.
Challenge 7 - Customer Support and Engagement
High-Touch Customer Support: In the early days, Zapier’s founders were heavily involved in providing personalized support to users. While this was essential for gathering feedback and refining the product, it was also resource-intensive and difficult to scale.
- Impact: The founders’ hands-on approach was unsustainable as the user base grew, stretching the team thin and limiting their ability to focus on other aspects of the business.
Building a Community: Engaging with users and creating a community around the product was crucial for Zapier’s growth. However, building these relationships required a significant commitment of time and resources.
- Impact: The need to foster a community while also growing the business created a strain on the small team.
Challenge 8 - Limited Funding
One of the earliest and most persistent challenges for Zapier was operating with limited funding.
Bootstrapped Growth: Unlike many of its competitors, Zapier chose to bootstrap its growth, raising only $1.3 million in funding by 2014. This decision to remain capital-efficient meant that Zapier had to stretch every dollar, making it difficult to invest heavily in marketing, product development, and infrastructure.
- Impact: The lack of substantial venture capital limited Zapier’s ability to scale as aggressively as some of its competitors. Marketing efforts were constrained, which slowed down user acquisition in the early years.
As Zapier continued to scale, maintaining platform stability and customer satisfaction was crucial. From operating with limited funding and scaling a complex product to navigating intense competition and maintaining a strong user experience, these obstacles required strategic thinking and relentless execution
Growth Strategies
Over the years, the Zapier team has implemented a series of innovative growth strategies that have taken it from a just bootstrapped startup to a leader in the automation space.
Here’s a look at the key strategies Zapier has employed at different stages of its journey.
Early Years (2011-2015)
1. Freemium Model (2015)
Zapier made a pivotal shift from a pay-to-use model to a freemium model, allowing users to access basic features at no cost. This was a game-changer.
Impact:
- The freemium model lowered the barrier to entry, enabling a wider audience to try out Zapier without financial commitment.
- This approach significantly boosted user acquisition as more people experimented with the platform, eventually leading to higher conversions to paid plans as users realized the value of the premium features.
2. Customer-Centric Development
From the beginning, Zapier’s founders engaged directly with users in forums and online communities. They didn’t just listen; they acted on the feedback.
- Impact:
- By understanding the specific needs and pain points of their users, Zapier was able to build features that directly addressed these concerns.
- This customer-centric approach not only improved user satisfaction but also fostered loyalty, as users felt their voices were being heard and their needs met.
Growth Phase (2016-2020)
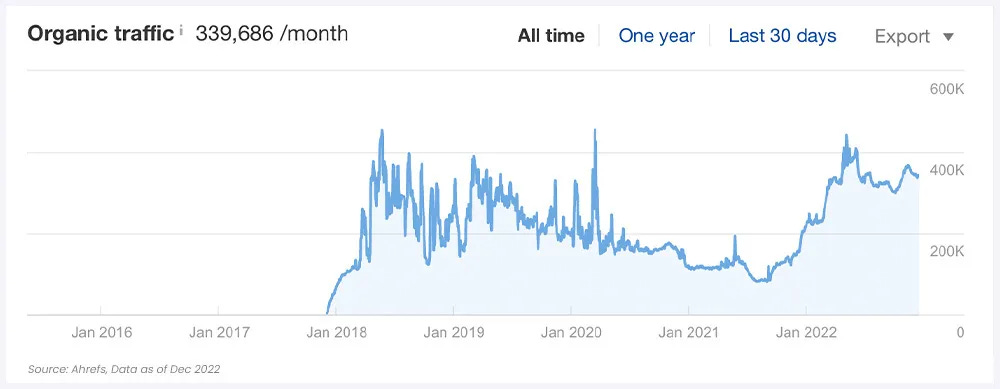
3. Programmatic SEO (2016-2021)
Zapier developed a robust SEO strategy that involved creating thousands of landing pages optimized for specific app integrations. This was a highly scalable approach.
- Impact:
- This initiative led to a dramatic increase in organic traffic, with Zapier reaching over 6 million unique visitors per month and 7x increase in traffic.
- By ranking for over 30,000 keywords, Zapier became a dominant force in organic search, driving massive user acquisition and establishing itself as a go-to solution for automation.
Challenges they fixed:
Vulnerability to Algorithm Changes: Zapier’s heavy reliance on SEO for user acquisition was a double-edged sword. While it drove substantial traffic, it also made the company vulnerable to the whims of search engine algorithms. They diversified their user acquisition once they started seeing algorithms fluctuating their traffic.
4. Content Marketing and Backlinking
Zapier didn’t just rely on SEO; they complimented it with strong content marketing and backlinking strategies. The focus was on creating valuable, evergreen content that would attract and retain users.
- Impact:
- The content strategy helped position Zapier as a thought leader in the automation space, further driving organic traffic.
- High-quality content combined with strategic backlinking enhanced Zapier’s authority in search engines, contributing to sustained growth in visibility and user acquisition.
5. Partnerships and Co-Marketing
Zapier formed strategic partnerships with other SaaS companies, engaging in co-marketing efforts that expanded their reach and introduced Zapier to new audiences.
- Impact:
- These partnerships allowed Zapier to tap into the user bases of their partners, accelerating growth.
- Co-marketing campaigns not only boosted brand awareness but also drove user acquisition by showcasing the seamless integration capabilities of Zapier.
Recent Developments (2021-Present)
6. Sales-Assisted Model
As Zapier matured, they introduced a sales-assisted model aimed at targeting larger enterprises and moving upmarket. This was a strategic shift from their initial focus on self-service.
- Impact:
- The sales-assisted approach opened up a new segment of customers, including larger enterprises that required more personalized solutions.
- This strategy contributed to a significant increase in average revenue per user (ARPU) and helped Zapier secure high-value contracts.
7. Enhanced Customer Support and Resources
Recognizing the importance of customer experience, Zapier invested heavily in customer support. They also built a comprehensive resource hub that included tutorials, webinars, and guides.
- Impact:
- Improved customer support led to higher retention rates as users felt supported and could easily find solutions to their problems.
- The resource hub empowered users to make the most of Zapier’s features, driving engagement and reducing churn.
8. Remote Work Culture
Zapier embraced a fully remote work model from the very beginning, allowing them to hire talent from anywhere in the world. This decision was ahead of its time and gave them a competitive edge.
- Impact:
- The remote work culture enabled Zapier to build a diverse and skilled team, fostering innovation and responsiveness to market needs.
- It also allowed for operational flexibility, which was particularly advantageous during the COVID-19 pandemic when remote work became the norm.
Zapier’s growth strategies have been a mix of innovative approaches and strategic pivots that adapted to the company’s evolving needs. From leveraging the freemium model and focusing on customer-centric development in the early years to adopting programmatic SEO and forming strategic partnerships during their growth phase, every move was calculated to drive user acquisition and retention.
Examples of Zapier’s Content Marketing Strategies
Zapier’s content marketing strategy is a key driver of its growth and brand visibility. By leveraging a variety of content formats and promotion techniques, Zapier has effectively engaged its audience, driven traffic to its platform, and increased awareness of its automation tools.
Below are some specific examples of how Zapier promotes its content to achieve these goals.
1. Listicle Promotion
Zapier regularly creates and promotes listicle posts on social media to attract traffic and engage their audience. These “best of” lists are not only informative but also optimized for search engines, making them a valuable part of their content strategy.
- Example: Zapier shared a tweet promoting their post on the "Best Project Management Software." The tweet highlighted the SEO success of the post, noting that it ranked 1 for the relevant keyword.
- Impact:
- This type of promotion drives significant traffic to their website, as users searching for top tools or software are likely to click on a highly-ranked listicle.
- The tweet also serves as social proof, showcasing Zapier’s authority on the topic and encouraging more clicks from their followers.
2. Internal Linking
Zapier uses internal linking strategically within their content to keep readers engaged and guide them towards additional relevant resources and product pages. This approach not only enhances the user experience but also boosts SEO by increasing the time users spend on their site.
- Example: In their "Best Productivity Apps" post, Zapier includes an eye-catching banner linking to another post on automating tasks. This banner not only draws attention but also subtly encourages readers to explore how Zapier’s products can help them streamline their workflows.
- Impact:
- Internal linking helps to keep readers on the Zapier website longer, increasing the likelihood of conversion.
- It also improves the SEO performance of linked pages, helping them rank higher in search engine results.
3. Partner Promotion
Zapier’s partner promotion strategy is a powerful way to expand their reach by leveraging the audiences of their integration partners. Co-marketing efforts ensure that both Zapier and their partners benefit from increased visibility and user engagement.
- Example: When onboarding a new integration partner, Zapier provides a clear set of promotional guidelines. These include suggestions like writing a blog post, sending an email to the partner’s mailing list, posting on social media, and hosting a webinar.
- Impact:
- This collaborative approach helps drive awareness of Zapier’s integrations among the partner’s audience, potentially leading to new users.
- By featuring partners prominently on their website, such as the Dropbox integration page, Zapier further enhances the visibility of these collaborations and reinforces their value proposition.
4. Engaging Content
Zapier goes beyond just promoting its product; it creates content that resonates with its audience’s broader interests. By producing educational and engaging resources, Zapier positions itself as a thought leader in productivity and automation.
- Example: Zapier’s "How I Work" blog series is a popular feature where they interview productivity experts about their workflows. This content is highly engaging and appeals to a wide audience interested in improving their efficiency, even if they’re not currently using Zapier.
- Impact:
- This type of content helps Zapier stay top-of-mind with potential customers, establishing them as a trusted resource in the productivity space.
- By promoting these posts on social media, Zapier drives readership and encourages sharing, further extending their reach and influence.
By effectively promoting their content across different channels and formats, Zapier has successfully driven traffic, generated leads, and built a strong brand presence in the automation market.
Product Strategies
Over the years, Zapier has implemented a variety of innovative product strategies and initiatives to enhance its platform, drive growth, and solidify its position as a leader in the automation space.
Below is a detailed overview of these strategies and their impact on the company's growth.
1. Developer Platform Launch (2012)
Recognizing the need to scale its integration offerings rapidly, Zapier launched a developer platform in 2012. This platform empowered third-party developers to build their own integrations with Zapier, significantly expanding the range of applications that could be connected through the platform.
Process:
Zapier provided developers with the tools, APIs, and documentation necessary to create integrations efficiently.
The platform encouraged widespread participation by offering visibility and access to Zapier’s growing user base
Impact:
This initiative was a game-changer, allowing Zapier to grow its integration library to over 6,000 apps.
The rapid expansion of available integrations made Zapier an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to automate workflows across a diverse set of applications, significantly enhancing its value proposition and market reach.
2. AI-Powered Automation (2023)
- Overview: In 2023, Zapier integrated AI capabilities into its platform to further simplify the creation of automated workflows. These features included natural language processing (NLP) to make automation setup more intuitive and accessible.
Process:
AI-powered features like automated Zap suggestions helped users identify the best workflows for their needs.
NLP enabled users to describe their automation goals in plain language, with Zapier translating these into actionable workflows.
Impact:
The incorporation of AI made the platform more user-friendly, especially for non-technical users, thereby broadening Zapier’s appeal.
This innovation positioned Zapier as a leader in the automation space, demonstrating its commitment to leveraging cutting-edge technology to enhance user experience.
3. Zapier for Teams (2019)
- Overview: To cater to the needs of organizations and collaborative teams, Zapier launched "Zapier for Teams" in 2019. This product was designed to facilitate collaboration by allowing team members to share and manage Zaps collectively.
Process:
The platform provided tools for team management, including shared folders, role-based access, and collaborative workflow editing.
It also offered advanced features tailored for business environments, such as team-wide usage analytics and centralized billing.
Impact:
Zapier for Teams targeted businesses and organizations, increasing engagement and retention within teams.
By facilitating collaboration, this initiative not only improved user satisfaction but also drove revenue growth by encouraging organizational adoption.
4. Makerpad Acquisition (2021)
- Overview: In 2021, Zapier acquired Makerpad, a leading no-code education platform. This acquisition was part of Zapier’s broader strategy to support the no-code movement and empower users to create automations without the need for coding skills.
Process:
Makerpad’s educational resources were integrated into Zapier’s ecosystem, offering tutorials, guides, and community support for no-code enthusiasts.
The acquisition also enabled Zapier to reach a broader audience by providing educational content that demystified automation and encouraged experimentation.
Impact:
The acquisition of Makerpad reinforced Zapier’s position as a leader in the no-code space, helping to democratize access to automation tools.
It also expanded Zapier’s community and user base by appealing to a wider audience interested in learning about and implementing no-code solutions.
5. Zapier Interface Designer (2021)
- Overview: To further enhance user experience and customization, Zapier introduced the Zapier Interface Designer in 2021. This tool allows users to create custom interfaces for their Zaps, making it easier to manage and interact with complex workflows.
Process:
The Interface Designer offered a drag-and-drop interface that users could customize to fit their specific workflow needs.
It enabled users to create dashboards and control panels tailored to their unique automation processes.
Impact:
The Zapier Interface Designer improved usability and customization, allowing users to optimize their workflow management.
This feature attracted more advanced users who needed greater control over their automation processes, further driving user engagement and satisfaction.
5 Key Learnings for Founders and Marketing Leaders from Zapier’s Growth Story
Zapier’s journey offers valuable insights for startups and marketing leaders looking to scale their businesses effectively. Here are ten key learnings, along with actionable steps for implementing these strategies in your startup.
1. Leverage Programmatic SEO for Scalable Growth
Learning: Zapier’s programmatic SEO strategy, which involved creating thousands of SEO-optimized landing pages, drove substantial organic traffic and user acquisition.
Implementation Steps:
- Step 1: Identify long-tail keywords relevant to your product or service that have lower competition but high intent.
- Step 2: Develop a system to automatically generate landing pages for each product feature, service, or integration that targets these keywords.
- Step 3: Optimize each page for SEO, ensuring that the content is relevant, informative, and includes user-generated content where possible.
- Step 4: Continuously monitor and update these pages based on performance metrics and changes in search engine algorithms.
2. Adopt a Freemium Pricing Model to Drive User Acquisition
Learning: Zapier’s freemium model lowered the entry barrier, allowing users to try the platform for free, which led to higher conversion rates.
Implementation Steps:
- Step 1: Identify the core features of your product that can be offered for free without compromising the value of your paid tiers.
- Step 2: Design a tiered pricing structure that encourages users to upgrade as they require more advanced features or increased usage.
- Step 3: Provide a clear value proposition for upgrading, such as access to premium features, increased support, or enhanced performance.
- Step 4: Monitor user behavior to identify when users are most likely to upgrade, and trigger targeted messaging or offers at these moments.
3. Focus on Content Marketing and Educational Resources
Learning: Zapier’s content marketing strategy, including blog posts, tutorials, and a learning center, helped educate users and drove traffic.
Implementation Steps:
- Step 1: Create a content plan that includes educational blog posts, tutorials, and use cases that demonstrate the value of your product.
- Step 2: Develop in-depth resources like eBooks, webinars, or a learning center to provide ongoing education for your users.
- Step 3: Optimize all content for SEO to ensure it reaches a broader audience through organic search.
- Step 4: Use content to address common pain points or questions from your users, positioning your brand as a trusted resource.
4. Engage in Micro-Marketing and Community Building Early On
Learning: Zapier’s founders engaged with potential customers in online forums, building early traction and gathering valuable feedback.
Implementation Steps:
- Step 1: Identify online communities, forums, and social media groups where your target audience gathers.
- Step 2: Actively participate in these communities by answering questions, providing value, and sharing insights without being overly promotional.
- Step 3: Use feedback gathered from these interactions to refine your product, messaging, and marketing strategies.
- Step 4: Build relationships with early adopters who can become advocates for your brand and provide valuable word-of-mouth marketing.
5. Leverage Partnerships and Co-Marketing Initiatives
Learning: Zapier’s partnership marketing strategy expanded its reach by tapping into the customer bases of partner companies.
Implementation Steps:
- Step 1: Identify potential partners whose products or services complement your own and whose customer base aligns with your target market.
- Step 2: Develop co-marketing initiatives, such as joint webinars, blog posts, or email campaigns, to promote each other’s products.
- Step 3: Provide partners with the resources and support they need to effectively market your integration or collaboration.
- Step 4: Track the performance of these initiatives to understand what works best and refine future partnerships accordingly.
Conclusion
The success of Zapier can be attributed to a combination of strategic foresight, user-centric product development, and innovative marketing practices. By implementing these learnings, founders and marketing leaders can better position their startups for growth, build strong customer relationships, and create sustainable business models that adapt to an ever-changing market landscape.
Loved this post?
Featured Posts
There is a reason why more than 40% of community initiatives fail…
Validating Problem, not Solution
If you’re not a subscriber, here’s what you missed earlier:
Subscribe to get access to the latest marketing, strategy and go-to-market techniques . Follow me on Linkedin and Twitter.