Bootstrap to $100M First Round in 8 Years - Grammarly Growth Story
Learn how Grammarly built a growth story for 8 years before raising their first round with 7 Mn Daily Active Users. Let’s analyze how they mastered freemium, platform integrations, and marketing.
Announcement
I just released a free assessment - “Growth Assessment - Find Your Perfect Path”
It has already helped more than 30 founders stop wasting time on the wrong growth tactics.
Here’s what makes it different:
P.S. - I’m giving this away for free because I built 4 companies and learned this lesson the expensive way, so you shouldn’t have to
It’s strange to see how a simple writing tool “Grammarly” became a unicorn..
Their stories always amused me. So, I decided to do research and break down their journey, focusing on key milestones, inflection points, and the driving forces behind their success.
Grammarly was founded in 2009 by Alex Shevchenko and Max Lytvyn as a bootstrapped startup.
Initially, Grammarly focused on selling to the enterprise market, such as universities, to generate revenue and improve the core product.
By 2013, Grammarly had achieved 2,326% revenue growth from 2009 and over 3 million registered users.
Transition to Freemium Model (2013-2015)
In the early 2010s, Grammarly transitioned to a freemium business model, offering a free browser extension while also selling a premium subscription.
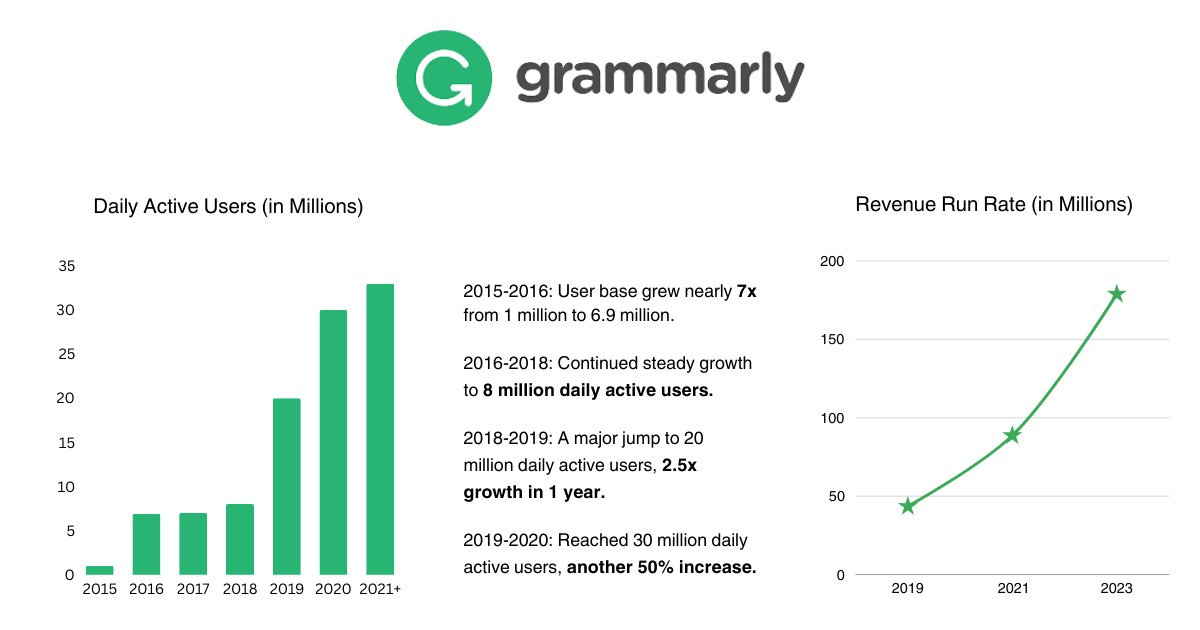
This freemium model helped drive massive user growth, going from 1 million daily active users in 2015 to 30 million by 2020.
Expanding Platform Integrations (2015-2019)
Grammarly released integrations for Microsoft Office, Google Docs, and various web browsers, making the tool more accessible and reducing friction for users.
This expansion of platform integrations further accelerated Grammarly's user and revenue growth.
By 2019, Grammarly had 6.9 million daily active users.
Grammarly's revenue grew from $43.5M in 2019 to $88.7M in 2021, a 104% increase.
Raising Funding and Scaling (2017-2021)
In 2017, Grammarly raised its first external funding of $110 million, reaching a $1 billion valuation.
This allowed Grammarly to further invest in product development and marketing to drive continued growth.
Grammarly raised additional funding rounds of $90 million in 2019 and $200 million in 2021, reaching a $13 billion valuation and becoming one of the top 10 most valuable U.S. startups.
As of 2022, Grammarly claims to have over 30 million daily active users globally.
As of 2023, Grammarly reported a revenue run rate of $178.9 million, representing 98.74% year-over-year growth.
Challenges
But the journey wasn’t that smooth either.. However, since they were building exactly as per “Job-to-be-done”, they faced some challenges during product massive usage…
Some users reported compatibility problems with Grammarly's browser extension, leading to slowdowns or glitches in certain web applications.
Users occasionally found Grammarly's vocabulary enhancement suggestions less relevant. Some synonyms didn't fit well, and the text similarity detection needed improvement. Additionally, suggestions were not always 100% accurate and required manual checking,
To keep up with the needs of a growing user base, Grammarly needed to continuously innovate to serve a global audience.
Growth Funnel
The funnel is simple for Grammarly.
Aware (Marketing) → Acquire (Marketing) → Easy Setup (Product) → Immediate Value (Product) → Gratification (Product) → High Utility (Product) → Convert (Marketing & Product)
They knew they had a solid product with an easy setup and immediate gratification. As people start using it, they see the value, and it becomes a high-frequency utility.
How did they acquire users?
Grammarly team has pulled off various marketing campaigns and initiatives across different channels:
I have analyzed them by pre-funding and post-funding phases:
Pre-Funding (Bootstrap) Phase (2009-2017)
This caught my attention as I was researching…
1 million daily active user in 2015 to 7 million daily active users in 2017
SEO and Content Marketing:
Grammarly focused on creating in-depth, informative content on their blog to rank for high-intent keywords related to writing assistance, grammar tips, and vocabulary improvement.
Example: Grammarly's early blog posts covered topics like "Affect vs. Effect" and "How to Write a Thesis Statement", providing valuable information to users while also boosting SEO.
Social Media:
Grammarly was more selective with its social media presence in the early years, focusing on building a following organically.
Example: In 2017, Grammarly launched the "Write the Future" campaign on social media, featuring a series of video ads demonstrating how their tools could help users achieve their goals through effective communication.
Partnerships and Integrations:
Grammarly worked on developing integrations with popular productivity tools like Microsoft Office and Google Docs to make the product more accessible to users.
Example: Grammarly promoted these early platform integrations through content marketing and in-product messaging to reduce friction and drive adoption.
Email Marketing:
Grammarly used email marketing to activate users, sending welcome emails, product updates, and educational content to help them get the most out of the tool.
Example: Grammarly's email campaigns focused on highlighting new features and encouraging users to upgrade to the premium subscription.
Welcome email
Post-Funding (Investment) Phase:
Paid Advertising:
Grammarly significantly ramped up its investment in display advertising, spending an estimated $210 million on these campaigns over the years.
Example: In 2023, Grammarly ran a $16.8 million YouTube ad campaign promoting its new generative AI feature, GrammarlyGO, which gained over 1.3 billion impressions in just 5 months.
Social Media Marketing:
Grammarly expanded its social media presence, launching accounts on platforms like TikTok and using a mix of informational and entertaining content to engage users.
Example: Grammarly's "Mental Health Awareness" campaign on social media (2019-present) aimed to build relationships with users and showcase how their tools can improve communication, which is important for mental health.
Branding and Awareness Campaigns:
Grammarly invested in larger-scale branding and awareness campaigns across multiple channels to reach new audiences and solidify its position as the leading writing assistant.
Example: Grammarly's "Grammarly for Professionals" campaign (2020) and "Grammarly for Students" campaign (2022) targeted specific user segments with tailored messaging and product features.
Continued Platform Integrations:
Grammarly expanded its platform integrations to make the tool more accessible and reduce friction for users.
Example: Grammarly promoted these new integrations through content marketing and in-product messaging to drive further adoption.
The key difference between Grammarly's pre-funding and post-funding marketing strategies was the scale and investment.
While the company initially focused on organic growth through content, partnerships, and email marketing, the funding allowed Grammarly to significantly scale its paid advertising, branding, and social media efforts to accelerate user acquisition and brand awareness.
What worked for Grammarly?
Freemium model → unlocked massive user adoption
Platform integrations → reduced friction, accelerated growth
Strategic funding rounds → aggressive scaling
Thoughtful content → spiked organic pull
What’s latest in Grammarly?
Strategic Suggestions:
Feature: Grammarly's Spring 2024 updates included "Strategic Suggestions" that provide personalized feedback based on the user's writing context and audience.
Example: Grammarly's AI can analyze an Outlook email and suggest changes to better convey the intended message and impact the recipient.
Improved Productivity
Feature: Grammarly introduced "App Actions" that allow users to access their favorite workplace apps (e.g., Asana, Slack) directly within the Grammarly interface.
Paragraph Rewrites:
Feature: Grammarly's new "Paragraph Rewrites" functionality can instantly edit entire sets of sentences, improving wording and correcting mistakes across multiple lines of text.
Fluency Enhancements:
Feature: Grammarly introduced "Fluency Enhancements" that provide suggestions to improve word choice and grammar, helping users sound more fluent in their English writing.
My take
1. Product-Led Growth Mastery
Grammarly's freemium model is a perfect example of product-led growth. By offering immediate value through a free browser extension, they created a low-friction entry point that drove massive user adoption.
Low Friction Setup → Immediate Value → High Utility
2. Strategic Integration as a Growth Lever
Grammarly's focus on platform integrations (Microsoft Office, Google Docs, browsers) was brilliant. By meeting users where they already work, they reduced adoption barriers and increased stickiness.
3. Content as a Dual-Purpose Asset
Grammarly's early focus on SEO and content marketing served two purposes: it drove organic growth and showcased the product's value. Their blog posts on writing tips weren't just marketing – they were product demonstrations.
4. Time your Funding (Chase it when you actually need it)
The contrast between Grammarly's pre-funding and post-funding strategies is super interesting to watch. While they built a solid foundation through bootstrapping, strategic funding allowed them to supercharge growth through aggressive marketing and product development.
Grammarly's story is a SaaS scaling blueprint. They nailed the balance between organic growth and smart investments, always putting user value first.
For us, it's a lesson in staying product-focused while growing market share.
Grammarly's next big test? Riding the AI wave without losing their edge.
Indie tools that you can try:
Whatlist -- Business, Networking and Group Engagement Co-pilot for Whatsapp
PostHog -- Product Analytics Platform for Developers to build and test new features
Featured Posts
If you’re not a subscriber, here’s what you missed earlier:
Subscribe to get access to the latest marketing, strategy and go-to-market techniques . Follow me on Linkedin and Twitter.